Adversarial Latent Autoencoders
- Stanislav Pidhorskyi et al., 2020, arXiv
- Keyword: Generative, Adversarial learning
- Problem: AE based approach has poor quality of output distribution.
- Solution: Adversarial setting and encoder, decoder decomposition.
- Benefits: Less entangled latent, sharp output distribution.
- Contribution: Learnable and less entangled latent with adversarial autoencoding structure.
- Weakness or Future work: -
GAN and AE
Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN)은 complex distribution을 표현하는 데 좋은 성능을 보여왔다. 특히 sharp 한 generation에 특이점을 가져 많은 현실적인 이미지나 음성을 생성할 수 있었다.
Autoencoder는 encoder, generator pair로 representation과 generation 모두를 포함하는 구조이다. 본문에서는 AE가 representation은 충분히 잘하고 있지만, generation까지 겸비한 모델은 아직 구현하지 못하였다고 이야기한다.
이에 소개하고자 하는 것이 Adversarial Latent Autoencoder (ALAE)이고, GAN과 비슷한 generative power를 가지면서도 representation disentangle이 가능한 모델을 목표로 한다.
대부분의 AE 연구들은 같은 가정을 하는데, latent space를 확률 분포로 모델링 하며, 이것을 고정된 prior에 맞춰야 한다는 것이다. 실제로 ELBO를 정의할 때 posterior q를 가정하고 variational inference를 진행하는데, KL-divergence가 대상으로 삼은 conditional prior가 intractable 하기 때문에 주로 고정된 prior를 사용하게 된다. 하지만 StyleGAN (Karras et al., 2018)에서는 분포상 제약을 받지 않고, 데이터로부터 학습된 latent space가 prior에서 많은 transform을 거칠수록, prior에서 거리가 멀어질수록, disentangle 하기 쉽다는 이야기를 한다.
여기서 착안하여 저자는 AE가 latent distribution을 data에서 학습할 수 있게 하였고, output distribution은 adversarial strategy를 통해 학습하였다. 이를 통해 GAN만큼의 generative power를 가지면서도 disentanglement를 더 용이하게 하는 것이다. 이는 근래 GAN 관련 분야에서 연구된 여러 기법이나 휴리스틱을 덜 사용하면서도 효과적으로 데이터를 모델링할 수 있게 한다.
Preliminaries: GAN Objectives
본문에서 소개하는 GAN objective의 general formulation은 다음과 같다.
$$V(\mathtt G, \mathtt D) = \mathbb E_{p_D(x)}\left[ f(\mathtt D(x)) \right] + \mathbb E_{p(z)}\left[ f(-\mathtt D(\mathtt G(z))) \right]$$
여기서 f를 softplus $f(t) = -\log(1 + \exp(-t))$로 두면 vanilla GAN과 같아지고, f를 identity $f(t) = t$로 두면 wasserstein GAN과 같아진다.
Adversarial Latent Autoencoders
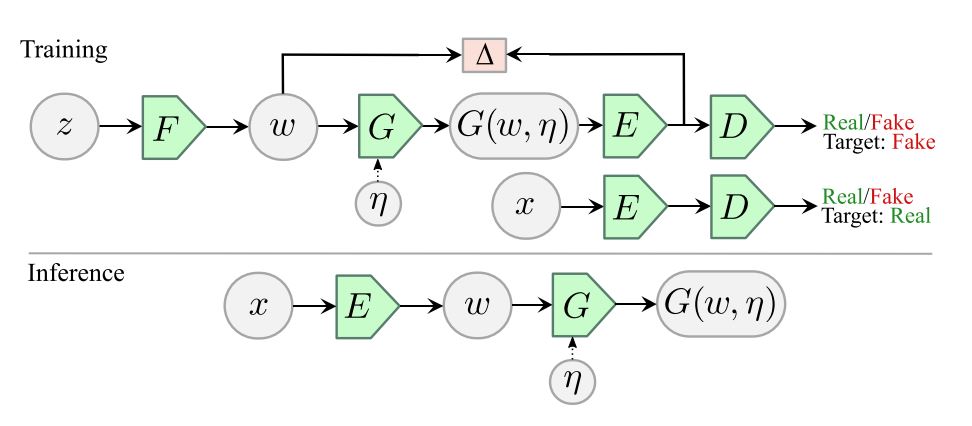
기존의 GAN이 generator와 discriminator를 single module로 구성하였다면, ALAE에서는 가장 먼저 G와 D를 $\mathtt G = G \circ F$와 $\mathtt D = D \circ E$로 분해한다. 그리고 F와 G 사이, E와 D 사이의 represenation을 latent W로 둘 것이다. 이 때 F와 D는 deterministic, G와 E는 stochastic하게 가정한다. G가 additional independent noise $\eta$를 받는다면 $G(w, \eta)$의 general stochastic generator가 될 것이다. 이때 G에서 생성된 output x의 확률은 다음과 같다.
$$q(x) = \int_w\int_\eta q_G(x|w, \eta) q_F(w) p_\eta(\eta) \mathrm d\eta \mathrm dw$$
마찬가지로 E에서 생성된 latent w의 확률은 다음과 같다.
$$q_E(w) = \int_x q_E(w|x)q(x)\mathrm dx$$
여기서 q(x)를 실제 데이터 분포 $p_D(x)$로 바꾼다면 데이터에 대한 latent $q_{E, D}(w)$가 될 것이다.
여기서 앞서 소개한 GAN objective를 토대로 모델을 학습한다면 이는 synthetic distribution q(x)를 실제 데이터 분포 $p_D(x)$로 맞춰가는 작업이 된다. 여기에 더불어 ALAE에서는 하나의 조건을 더 걸게 되며, 이는 $q_F(w) = q_E(w)$로 latent distribution을 matching 하는 작업이다.
AE는 latent와의 bijection을 위해 reciprocity, 자기복원의 기능을 가지는데, 크게 $x=G(E(x))$로 data space 상에서의 복원이 있을 수 있고, $w=E(G(w))$로 latent space 상에서의 복원이 있을 수 있다. 전자의 경우는 두 분포의 차이를 나타내는 reconstruction error를 가지게 되고, 각 픽셀을 독립된 확률 분포로 가정했을 때 prior에 따라 log-prob으로 l1이나 l2 loss를 띌 수 있다. 대부분의 AE 기반 모델에서 사용하지만 실제로는 blur나 noise 같은 output distribution에 표현되는 perceptual 한 손실을 만들기 때문에 지금까지의 AE 모델들이 쉽게 GAN에 비견되는 품질을 가질 수 없었다.
반면 ALAE는 후자를 선택하였는데, latent space 상에서 차이를 나타내는 discrepancy measure를 두고, F와 EGF의 출력을 비교하는 것이다. output 상에서의 l2-loss는 human perception을 반영하기보다는 단순 픽셀 상의 차이에 집중하고, 이런 한두 개의 픽셀 차이는 latent 상에 작용하기 어려워야 한다. 이에 latent 상에 직접 discrepancy measure를 걸어 버리는 것이 human perception에 더 직접적으로 작용할 수 있게 학습하는 것이다.
이는 GAN의 intuition과 비슷한데, GAN은 기존의 AE가 output space 상에서 independent 한 픽셀을 가정하고 discrepancy를 측정한 것에 반해, discriminator라는 human perception을 대체할만한 추가 모델을 두고, receptive field와 인지 능력을 학습받은 adaptive discrepancy를 측정할 수 있게 한 것이다.
ALAE에서는 이 discrepancy measure를 단순 l2로 두었는데, 이는 latent W에 어떠한 제약도 두고 싶지 않았기 때문이라고 한다. latent W에 distribution을 가정하고 KL-divergence와 같은 척도를 이용할 수도 있지만, 이렇게 되면 실상 F가 identity map과 같아지고 그 의미가 무색해진다. 대신 l2를 사용하였기 때문에 실제 데이터에 대한 latent $q_{E, D}(w)$와의 비교는 어려워졌다.
inference에서는 E로 input data를 encoding 하여 만든 latent w와 G를 통해 이미지를 재생성하는 방식으로 작동한다.
(StyleALAE에 대한 이야기는 보류한다.)
Detail
$L^{E, D}_ {adv} = \mathrm{softplus}(D\circ E \circ G \circ F(z)) + \mathrm{softplus}(-D \circ E(x)) + \frac{\gamma}{2}\mathbb E_{p_D(x)}\left[ ||\nabla D \circ E(x)||^2\right]$
$L^{F, G}_ {adv} = \mathrm{softplus}(-D\circ E \circ G \circ F(z))$
$L^{E, G}_ {err} = ||F(z) - E \circ G \circ F(z)||^2_2$
GAN objective의 f는 softplus를 사용하였고, 대신에 real data에 대한 gradient regularization term을 두었다. latent prior z는 standard gaussian으로 두었고, 따로 independent noise $\eta$를 두지 않은 것으로 보인다.
Discussion
실제로 MLP 기반의 MNIST 모델과 StyleALAE 기반의 여러 image synthesizing experiment를 진행하였고, image quality는 물론 latent 상에서의 preceptual path length가 짧아지는 등의 disentanglement 성능 향상도 보였다고 한다.
다른 연구들과는 달리 adaptive latent를 가정하여 less entangle한 latent를 학습할 수 있었고, adversarial setting으로 output distribution의 sharpness를 유지할 수 있었다. reciprocity에 대한 ablation study 같은 것이 있었으면 좋을거 같다.
Implementation
Reference
- Adversarial Latent Autoencoders, Stanislav Pidhorskyi et al., 2020.
- StyleGAN: A Style-Based Generator Architecture for Generative Adversarial Networks, Tera Karras et al., 2018.